What Is Basal Cell Carcinoma (BCC)
Basal cell cancer (BCC) is a form of skin cancer that affects the basal cells at the lower edge of your epidermis (outer skin layer) and often appears as a clear bump. When detected, it appears as either an irregular bump with glossy or dull surfaces. It typically grows gradually over time.
What Are Basal Cells? mess Basal cells can be found in the outermost layer of skin—where we can see and touch—where they produce new cells by dividing. As new ones form, old ones die off, moving closer to the surface where they die before eventually falling away naturally.
Are There Different Kinds of Basal Cell Carcinomas (BCCs)?
Basal cell carcinomas can be divided into four distinct subcategories:
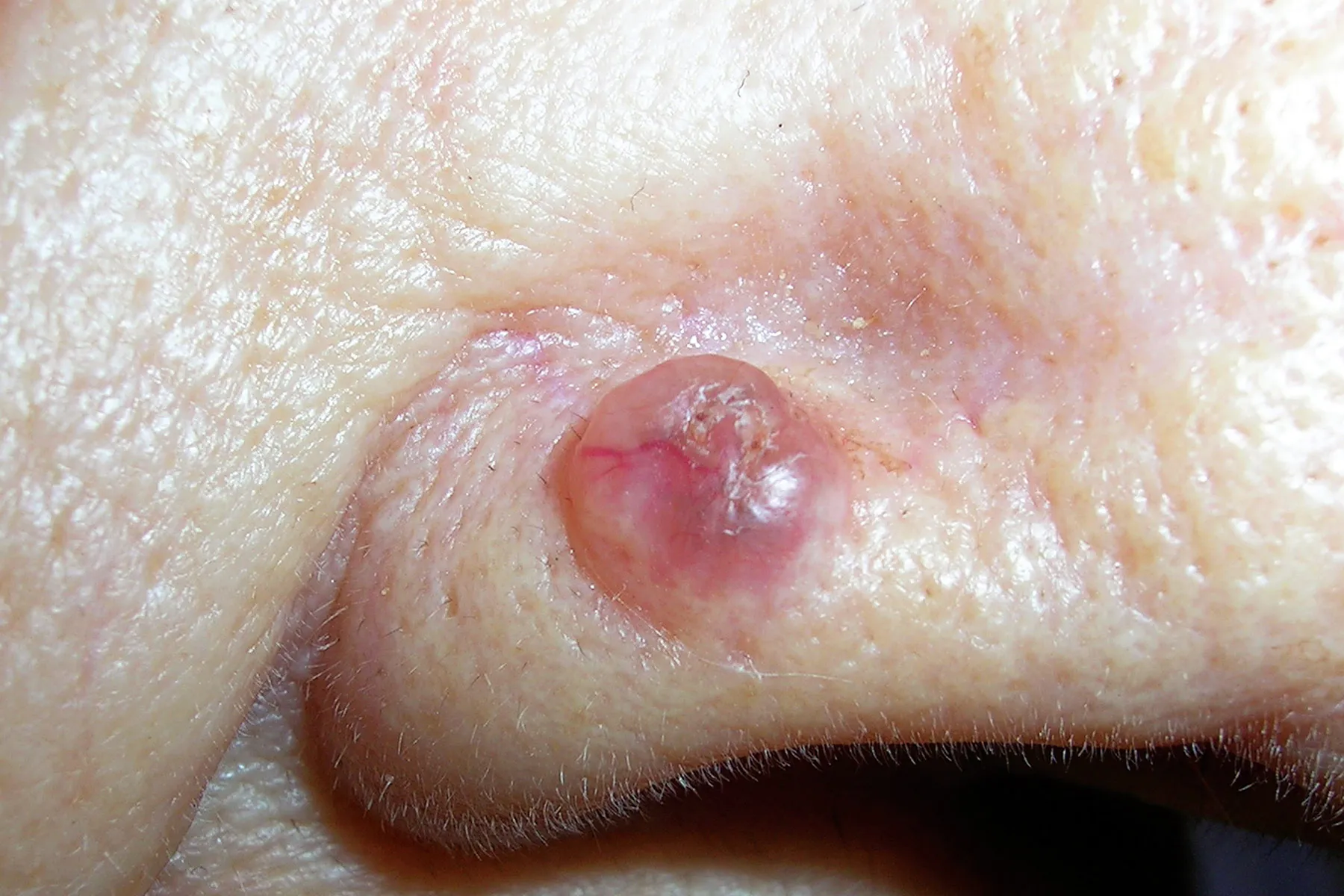
Nodular BCC: This form is the most prevalent. It appears as a small pimple with visible blood vessels known as telangiectasias.
Superficial BCC: These skin lesions appear as small spots with lighter than average pigmentation that typically appear on your trunk (torso), arms, or legs.
Sclerosing BCC: These lesions resemble scars and form slowly over time, with the occasional appearance of small red spots or smaller lesions on their surfaces.
Hyperpigmented BCC: This uncommon type results in darker patches on skin than are found nearby, distinguishable by contrast with surrounding tissue.
Who Is Affected By Basal Cell Cancer (BCC)?
Anyone can develop clear bump skin cancer, but it is more common in older adults with lighter skin tones and light-colored eyes. Once having had basal cell cancer (BCC), one’s risk for other non-melanoma skin cancer increases significantly should one ever recur later.
How common is basal cell carcinoma in the US?
Basal cell carcinoma is one of the most widespread forms of skin cancer; over 4 million new cases are diagnosed annually!
What Are The Signs and Causes Of Basal Cell Cancer (BCC)? Do I Suspect Basal Cell Cancer? Keep an eye out for skin changes like
- Bumps, pimples, or scabs.
- Any bump that appears clear, shiny, and compatible with your skin color, such as white, pink, brown, or black in tone.
- An apparent lump with small blood vessels.
- An undesired lump that grows bigger over time.
Clear bump skin cancer can be itchy and painful, especially when the bumps cause irritation, produce clear fluid, or bleed when touched.
Where Does Basal Cell Carcinoma Usually Develop?
Basal cell cancer typically manifests itself in areas exposed to sunlight, including
- What causes basal cell carcinoma? Basal cell cancer results from changes to your DNA caused by excessive UV radiation exposure from either sunlight or tanning beds.
- DNA gives your body the instructions it needs for making new cells; when damaged by UV rays, however, it sends wrong signals that direct basal cells to continue creating new ones when they should not, leading to too many cells being produced and possibly leading to lumps or patches on your skin.
- An extremely rare condition known as basal cell nevus (also referred to as Gorlin syndrome) may also contribute to BCC.
How is basal cell cancer diagnosis done?
Your physician will suspect BCC by the appearance of any bumps or lesions they see, then perform an exam and ask relevant questions like these:
- When did you first become aware of it?
- Have the conditions around this location changed over time?
- Do your clothes appear different now compared to before?
Are you itchy or hurting from something on your body? Have you experienced skin cancer before?
What Tests Can Be Performed to Diagnose Basal Cell Cancer?
- Skin Biopsy: Your physician takes a small sample from the spot under investigation and examines it under a microscope.
- Imaging Tests: Though BCC typically doesn’t spread, your physician may order an MRI or CT scan to check your lymph nodes and organs if he/she suspects this could have happened.
After conducting these tests, your physician will ascertain the stage of cancer by verifying certain parameters such as:
- Size and depth of tumor
If cancer cells have spread into lymph nodes, chemotherapy treatment will likely not work effectively as intended.
Clear bump skin cancer can become more serious if it has spread locally or to other parts of your body.
How fast the lesion is spreading:
- Shape, Size, and Location Considerations
Effective Treatment for Cancer Skin Peeling at Wall Dermatology
Protect your skin today with Wall Dermatology’s expert care. If you’re dealing with cancer skin peeling, our specialists provide personalized treatments for healing and prevention. Contact us now!
